27. 상속에서 클래스 생성 과정과 형 변환
| 하위 클래스가 생성되는 과정
하위 클래스가 생성될 때, 상위 클래스가 먼저 생성됨.
상위 클래스의 생성자가 호출되고, 하위 클래스의 생성자가 호출됨.
하위 클래스의 생성자에서는 무조건 상위 클래스의 생성자가 호출돼야함.
하위 클래스에서 상위 클래스의 생성자를 호출하는 코드가 없는 경우. 컴파일러는 상위 클래스 기본 생성자를 호출하기 위한 super() 를 추가한다.
super()로 호출되는 생성자는 상위 클래스릐 기본 생성자이다.
만약, 상위클래스의 기본 생성자가 없는 경우, ( 매개 변수가 있는 생서자만 존재하는 경우)
하위 클래스는 명시적으로 상위 클래스의 생성자를 호출해야한다.
| 상속에서의 메모리 상태
상위 클래스의 인스턴스가 먼저 생성이 되고
하위 클래스의 인스턴스가 생성된다.

package inheritance;
public class CustomerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// Customer customerLee = new Customer();
// customerLee.setCustomerName("이순신");
// customerLee.setCustomerID(1001);
// customerLee.bonusPoint=1000;
// System.out.println(customerLee.showCustomerInfo());
Customer customerKim = new VIPCustomer(100,"김유신2");
// customerKim.setCustomerName("김유신");
// customerKim.setCustomerID(1002);
customerKim.bonusPoint=120000;
System.out.println(customerKim.showCustomerInfo());
}
}
package inheritance;
public class Customer {
protected int customerID;
protected String customerName;
protected String customerGrade; // 자식이 쓸수 있게 p rotected
int bonusPoint;
double bonusRatio;
public Customer(int customerID, String customerName) {
this.customerID = customerID;
this.customerName= customerName;
customerGrade = "SILVER";
bonusRatio = 0.01;
System.out.println("customer 생성자 호출");
}
public int calcPrice(int price) {
bonusPoint += price * bonusRatio;
return price;
}
public String showCustomerInfo() {
return customerName + "님의 등급은 " + customerGrade + "이고, 적립된 보너스 포인트는 " + bonusPoint + "점 입니다.";
}
public int getCustomerID() {
return customerID;
}
public void setCustomerID(int customerID) {
this.customerID = customerID;
}
public String getCustomerName() {
return customerName;
}
public void setCustomerName(String customerName) {
this.customerName = customerName;
}
public String getCustomerGrade() {
return customerGrade;
}
public void setCustomerGrade(String customerGrade) {
this.customerGrade = customerGrade;
}
}
package inheritance;
public class VIPCustomer extends Customer {
private int agentID;
double salesRatio;
public VIPCustomer(int customerID, String customerName) {
super(customerID, customerName);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
customerGrade = "Gold";
bonusRatio = 0.05;
salesRatio = 0.1;
System.out.println("VIPcustomer int, name 생성자 호출");
}
// private int agentID;
// double salesRatio;
//
// public VIPCustomer() {
//
// //super();// this-> 자기 자신, super() -> 부모의 default 생성자의 호출
// super(0000,"Unknown"); // 부모의 default 생성자가 어뵤는 경우, 명시적으로 생성해 줘야한다.
// customerGrade = "Gold";
// bonusRatio = 0.05;
// salesRatio = 0.1;
// System.out.println("VIPcustomer 생성자 호출");
// }
}


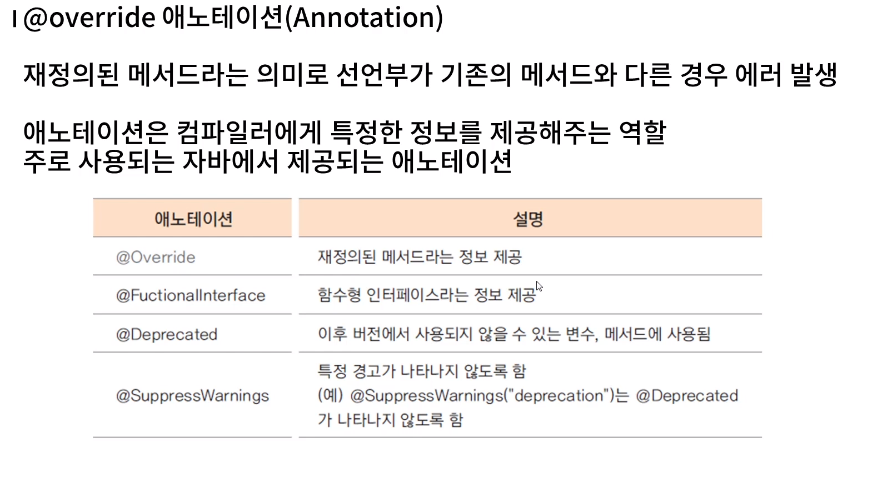
28. 매서드 오버라이딩
| 하위 클래스에서 메서드 정의하기
오버라이딩(overriding)
: 상위 클래스에 정의된 메서드의 구현 내용이 하위 클래스에서 구현할 내용과 맞지 않는 경우 하위 클래스에서 동일한 이름의 메서드를 재정의 할 수 있음.

package inheritance;
public class VIPCustomer extends Customer {
private int agentID;
double salesRatio;
public VIPCustomer(int customerID, String customerName) {
super(customerID, customerName);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
customerGrade = "Gold";
bonusRatio = 0.05;
salesRatio = 0.1;
System.out.println("VIPcustomer int, name 생성자 호출");
}
@Override
public int calcPrice(int price) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return (int) (super.calcPrice(price) * (1- this.salesRatio));
}
// private int agentID;
// double salesRatio;
//
// public VIPCustomer() {
//
// //super();// this-> 자기 자신, super() -> 부모의 default 생성자의 호출
// super(0000,"Unknown"); // 부모의 default 생성자가 어뵤는 경우, 명시적으로 생성해 줘야한다.
// customerGrade = "Gold";
// bonusRatio = 0.05;
// salesRatio = 0.1;
// System.out.println("VIPcustomer 생성자 호출");
// }
}

자바의 모든 메서드가 가상 메서드이다. 가상함수.
package inheritance;
public class OverridingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer customerLee = new Customer(99, "이순재");
customerLee.bonusPoint = 1000;
VIPCustomer customerKim1 = new VIPCustomer(100, "김유신1");
customerKim1.bonusPoint = 1000;
Customer customerKim2 = new VIPCustomer(100, "김유신2");
customerKim2.bonusPoint = 1000;
int priceLee = customerLee.calcPrice(10000);
int priceKim1 = customerKim1.calcPrice(10000);
int priceKim2 = customerKim2.calcPrice(10000);
System.out.println(customerLee.showCustomerInfo() + " 지불 금액은 " + priceLee + "원 입니다.");
System.out.println(customerKim1.showCustomerInfo() + " 지불 금액은 " + priceKim1 + "원 입니다.");
System.out.println(customerKim2.showCustomerInfo() + " 지불 금액은 " + priceKim2 + "원 입니다.");
/*
* customer 생성자 호출 customer 생성자 호출 VIPcustomer int, name 생성자 호출 이순재님의 등급은
* SILVER이고, 적립된 보너스 포인트는 1100점 입니다. 지불 금액은 10000원 입니다. 김유신2님의 등급은 Gold이고, 적립된
* 보너스 포인트는 1500점 입니다. 지불 금액은 9000원 입니다.
*
*/
}
}
| 가상 메서드( virtual method )
메서드 이름과 메서드 주소를 가진 가상 메서드 테이블에서 호출된 메서드의 주소를 참조함.
메서드 오버라이딩을 하면 메서드 주소 값이 바뀌어버림.

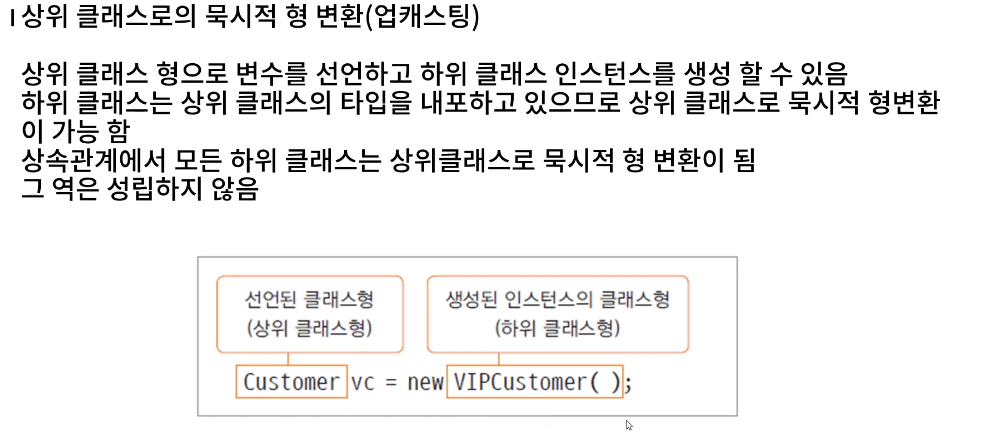
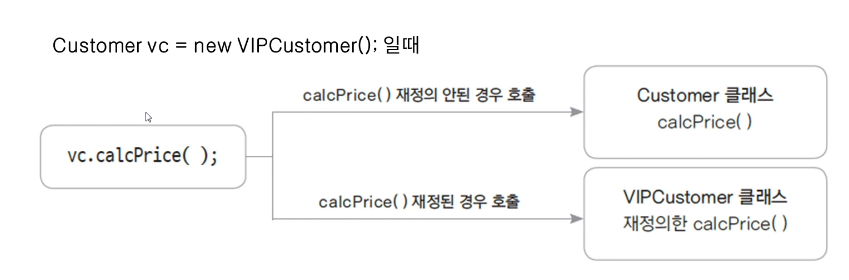
| 형 변환과 오버라이딩 메서드 호출
Customer vc = new VIPCustomer();
vc.calcPrice(10000);
위 코드에서 calcPrice() 메서드는 어느 메서드가 호출 될 것인가?
자바에서는 항상 인스턴스(VIPCustomer) 의 메서드가 호출된다.
| 재정의된 메서드의 호출과정
자바 인강이 듣고 싶다면 => https://bit.ly/3ilMbIO
'스프링, 자바' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [패스트캠퍼스 수강 후기] 자바 인강 100% 환급 챌린지 26회차 미션 (0) | 2020.09.04 |
|---|---|
| [패스트캠퍼스 수강 후기] 자바 인강 100% 환급 챌린지 25회차 미션 (0) | 2020.09.03 |
| [패스트캠퍼스 수강 후기] 자바 인강 100% 환급 챌린지 23회차 미션 (0) | 2020.09.01 |
| [패스트캠퍼스 수강 후기] 자바 인강 100% 환급 챌린지 22회차 미션 (0) | 2020.08.31 |
| [패스트캠퍼스 수강 후기] 자바 인강 100% 환급 챌린지 21회차 미션 (0) | 2020.08.30 |
